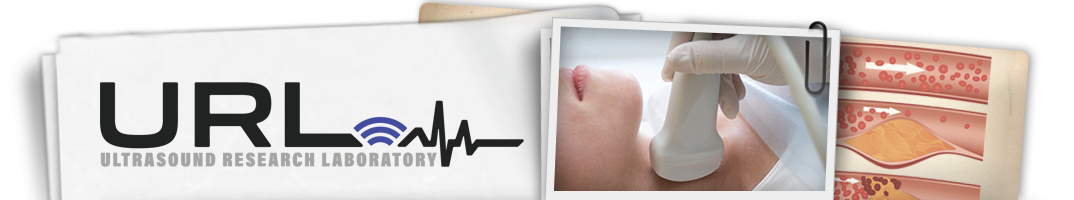
Carotid IMT
Methodology
Carotid duplex imaging is used to measure intima-media thickness (IMT), a measure of subclinical cardiovascular disease (CVD) which has been shown to correlate with CVD risk factors. Using a high resolution ultrasound system, detailed B-mode images of the right and left common carotid artery, common carotid bifurcation, and the first centimeter of the internal carotid artery are obtained. Selected images are digitized for later measurement of intima-media thickness. After imaging, the sonographer obtains pulse-wave Doppler measures of blood flow velocity at the mid common (2 cm proximal to the carotid bulb) and in the internal carotid artery at the point of highest velocity distal to the flow divider. These are used to calculate the degree to which plaque may be interfering with blood flow. The scanning and reading protocols result in three primary carotid disease measures: average wall intima-media thickness; a measure of degree of focal plaque called the plaque index; and the velocity ratio, a determination of whether or not plaque is interfering with blood flow in the internal carotid artery.
Protocol
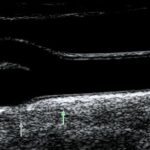 Our standard protocol includes IMT and plaque measurement from 5 bilateral segments of the carotid system. The sites are as follows:
Our standard protocol includes IMT and plaque measurement from 5 bilateral segments of the carotid system. The sites are as follows:
- From the take-off of the common carotid artery (CCA) to a point 2 cm’s proximal to the carotid bulb
- From 2 cm’s proximal to the carotid bulb, to the beginning of the carotid bulb
- From the beginning of the carotid bulb to the flow divider
- First centimeter of the internal carotid artery (ICA) measured from the tip of the flow divider
- First centimeter of the external carotid artery (ECA), measured from the tip of the flow divider
Plaque Grade
The degree of plaque is graded for each segment using the following criteria:
- Grade 0: no observable plaque
- Grade 1: one small plaque (less than 30% of the vessel diameter)
- Grade 2: one medium plaque (30-50% of the vessel diameter) or multiple small plaques
- Grade 3: one large plaque (greater than 50% of the vessel diameter) or multiple plaques with at least one medium plaque
Plaque Index
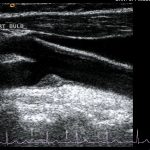
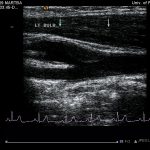 The plaque grades are then summed to create a variable called the plaque index, which is used as a measure of the extent of atherosclerosis.
The plaque grades are then summed to create a variable called the plaque index, which is used as a measure of the extent of atherosclerosis.
Reading IMT
B-mode images are electronically captured using customized image capture software developed at the URL. During the real-time scan, carotid B-mode images are digitized using a personal computer equipped with an image capture board. The images are stored on a network until IMT scoring is completed. Images are archived electronically on CD’s and DVD’s.
The lumen-intima and medial-adventitial interfaces are identified across 1 cm segments of the near and far walls of the common carotid artery and the far walls of the bulb and internal carotid arteries. This is done with Artery Measurement System, AMS, (Wendelhag et.al., Gothenburg, Sweden, 1991). The software automatically connects two interfaces generating an average of 140 IMT measures for each 1 cm segment. These are then averaged for an overall measure of IMT. Data are electronically filed and combined into a large database for analysis at the Graduate School of Public Health Data Center.